DBMS > Inroduction > What do you mean by Data Model?
Data Model:
Data models define how the logical structure of a database is modeled by the database architect. It is a description of the objects/entities represented by a computer system together with their properties, relationships and certain constraints that the database should obey. Output of data modeling is diagram that represents the data structure to support a new software application.
In the context of programming languages, data model sometimes refers as a data structure and in the context of enterprise models it is function models.
Data Modeling Process
Data modeling process involves three MAIN PHASES with different levels of detail: the conceptual data model, the logical data model, and the physical data model.
Conceptual (high-level, semantic) data models: The conceptual level is a way of describing what data is stored within the whole database and how the data is inter-related. The conceptual level does not specify how the data is physically stored. Some important facts about this level are ...
- DBA works at this level.
- Describes the structure of all users.
- Only DBA can define this level.
- Global view of database.
- Independent of hardware and software.
it is also called entity-based or Object-based data models.
Physical (low-level, internal) data models: Provide concepts that describe details of how the data is actually stored in the database and on the computer hardware.
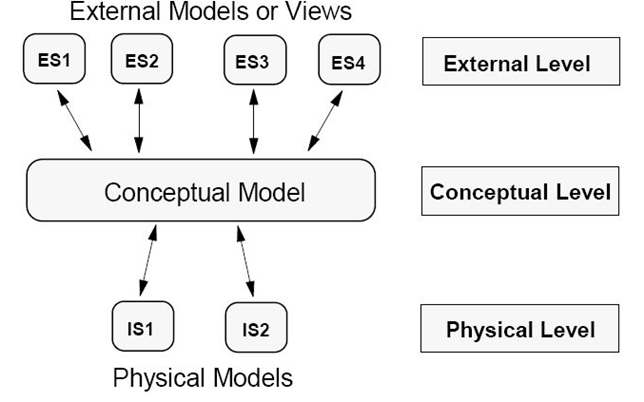
Implementation (representational) data models(External Level, User Views): Provide concepts that fall between the above two, balancing user views with some computer storage details. A user's view of the database describes a part of the database that is relevant to a particular user. It excludes irrelevant data as well as data which the user is not authorized to access.
What is single-tier, Two-tier and Three-tier Architecture of Software?
No More
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner