Information Theory and Coding > Data Compression > Explain Arithmetic Coding with example
Arithmetic Coding:
In arithmetic coding technique, a string of characters like the words “hello friends’ is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in ASCII code. When a string is converted to arithmetic encoding, frequently used characters are stored with fewer bits and not-so-frequently occurring characters are stored with more bits, resulting in relatively fewer bits used in total.
The steps of arithmetic coding algorithm are:
- Put the symbols in decreasing order of probabilities pi i ∈ I p1 ≥ p2 ≥···≥ pm
- Divide the interval [0; 1) into n intervals of dimensions p1, p2 ,···, pm
- Read the first symbol of the message and memorise its associated interval.
- Divide this interval into n intervals, each of them proportional to p1, p2 ,···, pm
- Read the next symbol and memorise the interval associated to it.
- Continue the process following the same algorithm.
- Transmit one number (Lower range) from the last memorised interval
Difference between Arithmetic Coding and Huffman Coding
|
Arithmetic Coding |
Huffman Coding |
|
Complex technique for coding short messages |
Simple technique |
|
Gives optimum result |
Does not give optimum result |
|
There is no one-to-one correspondence between source symbol and codeword |
There is one-to-one correspondence between source symbol and codeword |
|
Compression ratio is more |
Compression ratio is less |
|
Execution time is more |
Execution time is more |
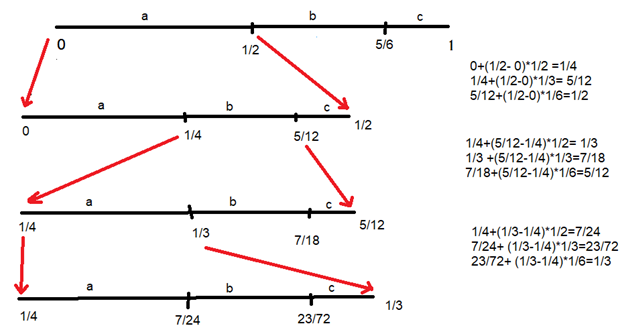
Example: Encode the message “abac” using an arithmetical code designed for the source S and probability of their occurrences are {a,b,c}={ 1/2 , 1/3 , 1/6}. Encode this string using arithmetic coding algorithm.
Encoding:
|
Processed Interval |
Read Symbol |
Memorised interval |
||
|
0 - 1/2 |
1/2 – 5/6 |
5/6 -1 |
a |
0 – 1/2 |
|
0 + (UL –LL)*Pr 0 + (1/2 -0)*1/2 =1/4 |
1/4 + (1/2 -0)*1/3 = 5/12 |
1/2
|
|
|
|
0 – 1/4 |
1/4 - 5/12 |
5/12 -1/2 |
b |
1/4 - 5/12 |
|
1/4 - 1/3 |
1/3 – 7/18 |
7/18 -5/12 |
a |
1/4 - 1/3 |
|
1/4 - 7/24 |
7/24 – 23/72 |
23/72 - 1/3 |
c |
23/72 -1/3 |
We may transmit a number from the interval [23/72; 1/3], for example 23/72.
Decoding: 23/72 is received
|
Processed Interval |
Interval Containing 23/72 |
Associated Symbol |
||
|
0 - 1/2 |
1/2 – 5/6 |
5/6 -1 |
0-1/2 |
a |
|
0 + (UL –LL)*Pr 0 + (1/2 -0)*1/2 =1/4 |
1/4 + (1/2 -0)*1/3 = 5/12 |
1/2
|
|
|
|
0 – 1/4 |
1/4 - 5/12 |
5/12 -1/2 |
1/4 -5/12 |
b |
|
1/4 - 1/3 |
1/3 – 7/18 |
7/18 -5/12 |
1/4 - 1/3 |
a |
|
1/4 - 7/24 |
7/24 – 23/72 |
23/72 - 1/3 |
23/72 - 1/3 |
c |
So decoding string is abac
What is Huffman Coding?
No More
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner