Fundamentals of Computer > Central Processing Unit (CPU) > Different parts of the CPU & Their Functions
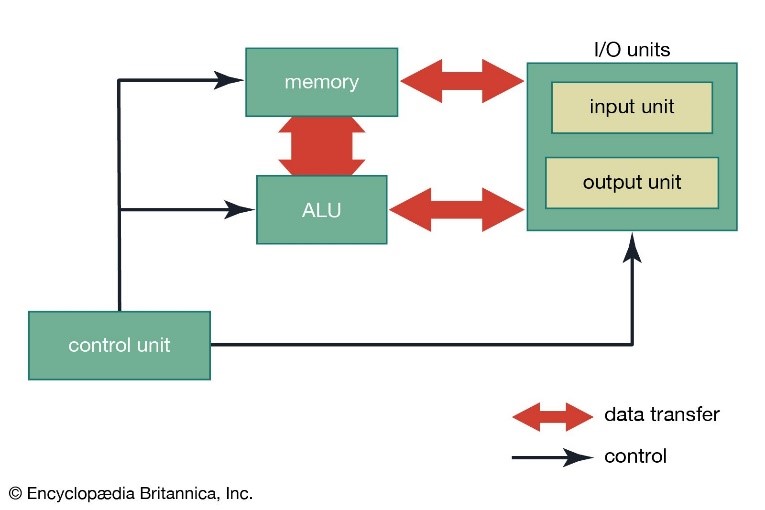
Every CPU has at least two basic parts:
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
- Control Unit
Moreover, memory is also referred to as the part of CPU.
The parts of the CPU are usually connected by an electronic highway known as ‘Bus’. To temporarily store data and instructions, the CPU has high-speed special-purpose memory devices called ‘Registers’.
The primary functions of ALU are:
- All arithmetic calculations and logical decisions are performed in the ALU.
- When needed for processing, ALU receives data and instructions (involving arithmetic or logical operations) from primary memory.
- ALU temporarily sends back the partial results to the primary memory, until needed later.
- After the processing is over, the ALU then sends the final result to the memory unit to be stored either permanently or temporarily.
The primary functions of Control Unit are:
- This unit controls and coordinates the activities of all other units of a computer system.
- It takes instructions from the memory unit one at a time and interprets them. It then sends appropriate signals to all other units to cause the specific instruction to be executed.
- According to the stored instructions, the control unit ensures that the right operation is done on the right data at the right time.
Control unit acts as a central nervous system although it does not perform any actual processing on the data.
The primary functions of Memory Unit are:
- Memory stores data and instructions received from the input device for processing.
- It supplies information to the ALU when required.
- It receives partial or final results from the ALU.
- It supplies final results to the output device.
Types of Processor
There are two well-known processor: RISC and CISC Processor.
CISC Processor (Complex Instruction Set Computer)
- It is a kind of microprocessor chip that typically contains 200 to 300 instructions in it.
- In this type of processor, the instruction sets are designed elaborately as complex way.
- Length of each instruction in this type of processor is of variable length.
- Variable length addressing modes are also used in CISC processor.
- The processors in IBM-compatible computers and Motorola 680x0 computers are CISC processors.
RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
- A newer theory in microcomputer design holds that if the instruction set for the CPU is kept small and simple, each instruction will execute much faster, allowing the processor to complete more instructions during a given period.
- CPUs designed according to this theory are called RISC processor (Reduced Instruction Set Computer). In this type of processors, reduced number of instructions is used (less than 200).
- Length of each instruction in this type of processor is of equal/ fixed length.
- Fixed length addressing modes are also used.
- This type of processor is used in the PowerPC computers.
RISC processor-based PC results in a faster and less expensive than that of CISC processor-based PC.
Coprocessor used in PC
A co-processor is a separate instruction-set processor that is closely coupled to the CPU.
- Its purpose is to enhance the processing speed of the main processor (CPU).
- Complicated arithmetic operations like exponentiation and trigonometric functions are costly to implement in the CPU hardware, while software implementations of these operations are slow. An arithmetic or math coprocessor is used as the auxiliary processor to the CPU to provide fast, low-cost hardware implementations of these special math functions.
Newer CPUs have math coprocessor built-in. Earlier CPUs did not have them, so many users choose to upgrade their machines by adding them.
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner