Machine Learning > Sampling > Define Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling
Define Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling.
We Know that all sampling units that are drawn from a distribution are independent samples, But in Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling samples are not independent. Like Markov Chain or process, where next event depends on current event, MCMC sampling are such sampling methods where the draw of next sample is dependent on the existing sample. This allows the sampling algorithms to narrow in on the quantity that is being approximated from the distribution, even with a large number of random variables.
Advantages of MCMC:
- Applicable even when we can’t directly draw samples
- Works for complicated distributions in high-dimensional spaces, even when we don’t know where the regions of high probability are
- Relatively easy to implement
- Fairly reliable
Disadvantages:
- Slower than simple Monte Carlo or importance sampling
- Can be very difficult to assess accuracy and evaluate convergence, even empirically
Suppose p(x, y) is a p.d.f. that is difficult to sample from directly. Suppose, though, that we can easily sample from the conditional distributions p(x|y) and p(y|x).
Algorithm of Gibbs sampling proceeds:
set x and y to some initial starting values, then sample x|y, then sample y|x, then x|y, and so on
- Set (x0, y0) to some starting value.
- Sample x1 ∼ p(x|y0), that is, from the conditional distribution X | Y = y0.
- Sample y1 ∼ p(y|x1), that is, from the conditional distribution Y | X = x1.
- Sample x2 ∼ p(x|y1), that is, from the conditional distribution X | Y = y1. Sample y2 ∼ p(y|x2), that is, from the conditional distribution Y | X = x2.
Each iteration (1., 2., 3., . . . ) in the Gibbs sampling algorithm is sometimes referred to as a sweep or scan. The sampling steps within each iteration are sometimes referred to as updates or Gibbs updates.
In Baysian Analysis, we need to calculate posterior probability.
What is the important properties of Baysian Analysis?
Example: Sampling from 2-d Normal distribution
The distribution of X and Y is N(µ, Ʃ) where
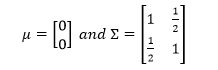
Sampling from this distribution is difficult. Probability distribution of P(X/Y) ~ N(y/2,3/4) and P(Y/X) ~ N(x/2, 3/4) is known.
Draw a Gibbs sample from this above joint population.
Solution:
- Let (x0, y0) =(.3 , .7)
- x1 ∼ p(x|y0)=p(x/y0=0.7) ~ N(y/2,3/4) ~ N(0.35, 3/4) -> 0.655 (say)
- y1 ∼ p(y|x1)=p(y/ x1=0.655) ~ N(x/2, 3/4) ~ N(0.327, 3/4) -> (say)
- Repeat

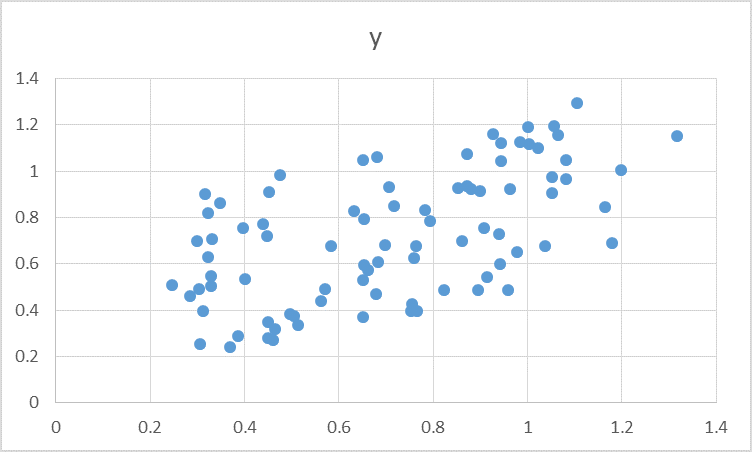
Sampling from Normal distribution using the Box-Muller Transformation of data from Uniform distribution
The Box-Muller transform allows us to sample from a pair of normally distributed variables using a source of only uniformly distributed variables. Given two independent uniformly distributed random variables U1, U2 on the interval (0,1),
X and Y are independent standard normally distributed random variables:
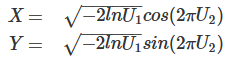
Continue using this above as much as we need sample. For N repetition we will get n pair of (X, Y) joint normally distributed data.
To find sample from normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation δ N(µ, δ) we have to further convert X and Y simultaneously: X=X δ + µ
Why does a Markov process is called memoryless process?
No More
Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner