Fundamentals of Computer > Central Processing Unit (CPU) > Bus System and Port Used in Microcomputer
ISA Bus (Industry Standard Architecture):
- This bus was developed by IBM (International Business Machine) for its personal computer.
- It is a 16 bit bus (At first it was 8 bit bus when developed)
- This bus is still used in many computers to attach slower devices (such as modems and input devices) to the CPU.
- It works significantly for 286 microprocessor-based computers.
EISA Bus (Enhanced Industry Standard Architecture)
- This bus is developed by a consortium of hardware developers.
- It is a 32 bit bus
- Expansion cards designed for ISA bus will run in the EISA slots.

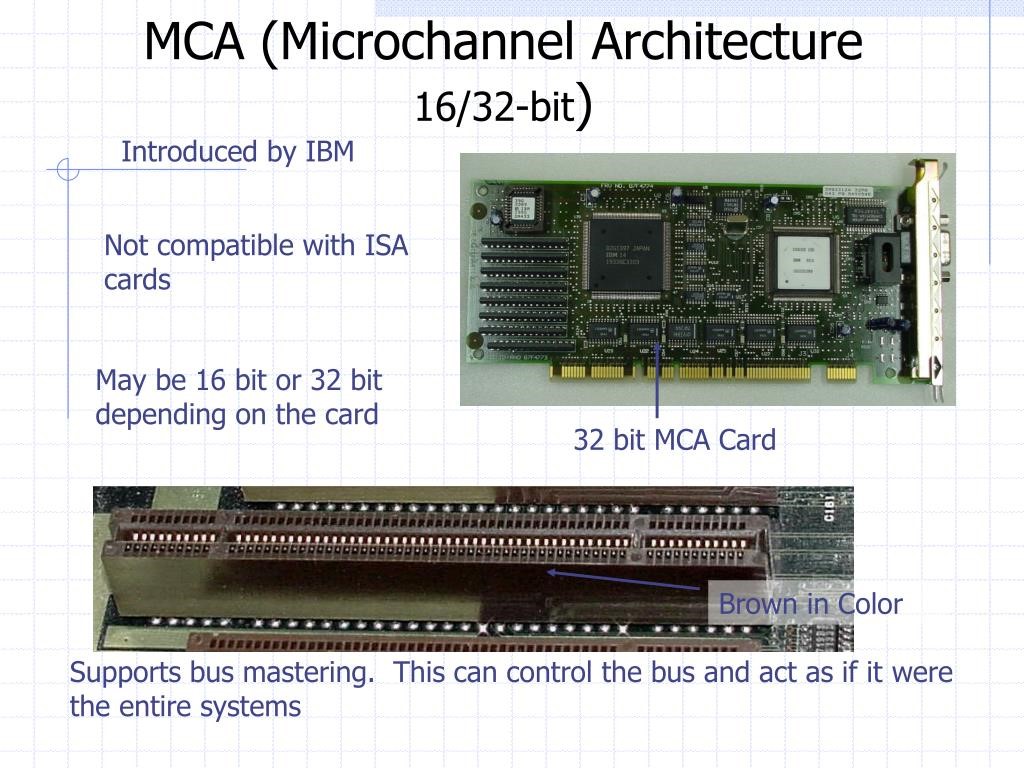
MCA Bus (Micro Channel Architecture)
- This bus was developed by IBM for its PS/2 microcomputer.
- It is a 32 bit bus
- Expansion cards designed for ISA bus or EISA bus do not run in the MCA bus slot.
- This bus was not backward compatible.
- It works significantly for 386 microprocessor-based computers.
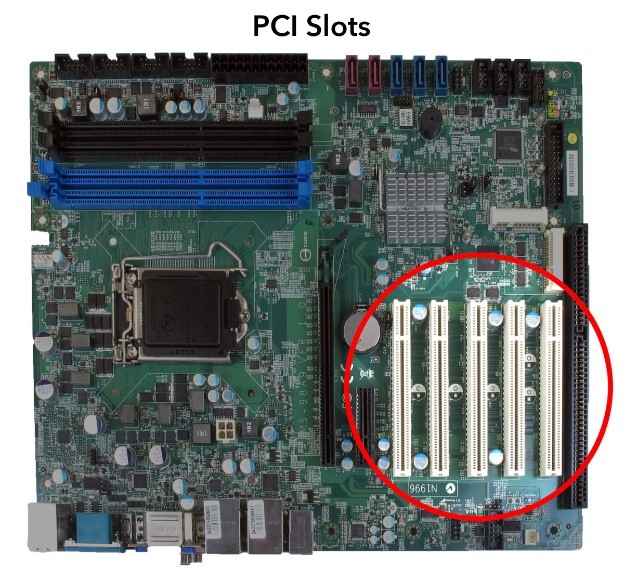
PCI Bus (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
- This bus is designed by Intel Corporation
- It is a 64 bit bus
- This bus was “open domain” i.e. allowing anyone to use it without Intel’s permission or any payment to Intel.
- This bus integrates new data types, such as audio, video, and graphics.
- It is widely used in high-speed Pentium-based computers.

USB Bus (Universal Serial Bus)
- This bus is connected to the PCI bus.
- USB was at first co-invented by Ajay Bhatt of Intel (an Indian-American computer architect) and the USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum, Inc). The organization is comprised of industry leaders like Intel, Microsoft, Compaq, LSI, Apple and Hewlett-Packard.
- Unlike the PCI bus, USB is a hot swappable bus. (Hot Swappable means, a user can connect and then disconnect a USB device without affecting the machine.
- It allows connecting lower speed I/O devices to PC such as mouse, keyboard, flash memory, etc. without having to go through a complex installation procedure.
- USB supports up to 127 devices connected in either a daisy chain or hub layout.
PCMCIA Bus
- This bus was developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA).
- It is a 32 bit bus.
- It allows user to insert credit card-size peripherals such as memory cards, modems etc.
- It is an open domain (i.e. allowing anyone to use it without permission), nonproprietary bus standard.
- This bus is used for notebook, sub-notebook and palmtop computers.
- A card used in this bus is now called PC Card.

Feedback
ABOUT
Statlearner
Statlearner STUDY
Statlearner